Tips and Pearls
· A significant proportion of patients with ventricular preexcitation remain asymptomatic yet at the risk of life-threatening arrhythmia
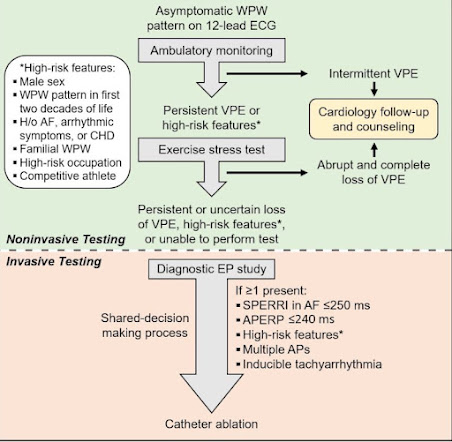
· Intermittent ventricular preexcitation during ambulatory monitoring or abrupt and complete termination of accessory pathway conduction during stress testing suggests a low-risk pathway.
· Shortest preexcited RR interval during AFib < 250 ms , or accessory pathway effective refractory period (APERP) < 240 ms suggest a high-risk pathway .
· Shared-decision making must be performed before offering catheter ablation .
Simplified approach to asymptomatic WPW evaluation
Wolff-Parkinson-White (WPW) preexcitation. A: Typical WPW preexcitation pattern manifesting as a short PR interval, delta wave , and a wide QRS complex. B: Loss of ventricular preexcitation (VPE) during noninvasive testing. C: Noninvasive shortest preexcited R-R interval (SPERRI) measurement during rapit preexcited AF that can be potentially precipitate VF . Courtesy of Kashou AH, Wackel PL, Kowlgi GN
References
- Page RL, Joglar, JA, Caldwell MA, et al. 2015 ACC/AHA/HRS guideline for the management of adult patients with supraventricular tachycardia: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines and the Heart Rhythm Society. J Am Coll Cardiol 2016;67:e27–e115.
- Cohen MI, Triedman JK, Cannon BC, et al. PACES/HRS expert consensus statement on the management of the asymptomatic young patient with a Wolff-Parkinson-White (WPW, ventricular preexcitation) electrocardiographic pattern. Heart Rhythm 2012;9:1006–24.
- Obeyesekere MN, Leong-Sit P, Massel D, et al. Risk of arrhythmia and sudden death in patients with asymptomatic preexcitation: a meta-analysis. Circulation 2012;125:2308–15.
- Etheridge SP, Escudero CA, Blaufox AD, et al. Life-threatening event risk in children with Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome: a multicenter international study. JACC: Clin Electrophysiol 2018;4:433-44.



No comments:
Post a Comment